
Mahim, Mumbai, India - 400016.
Verified
Details verified of Jyoti B.✕
 Identity
Identity
 Education
Education
Know how UrbanPro verifies Tutor details
Identity is verified based on matching the details uploaded by the Tutor with government databases.
Hindi
Marathi
English
![]() Mumbai University
Mumbai University
Master of Science (M.Sc.)
Mahim, Mumbai, India - 400016
![]() ID Verified
ID Verified
![]() Education Verified
Education Verified
![]() Email Verified
Email Verified
Report this Profile
Is this listing inaccurate or duplicate? Any other problem?
Please tell us about the problem and we will fix it.
Class Location
![]() Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
![]() Student's Home
Student's Home
![]() Tutor's Home
Tutor's Home
Years of Experience in Class 9 Tuition
7
Board
State, International Baccalaureate, ICSE, CBSE
Subjects taught
Biology, Chemistry, Social Science, Geography, EVS, Science, Environmental Applications, History, History and Civics, Hindi
Taught in School or College
No
Class Location
![]() Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
![]() Student's Home
Student's Home
![]() Tutor's Home
Tutor's Home
Years of Experience in Class 10 Tuition
7
Board
State, International Baccalaureate, ICSE, CBSE
Subjects taught
Environmental Applications, Biology, History and Civics, Science, EVS, Hindi, Geography, History, Chemistry, Social Science
Taught in School or College
No
Class Location
![]() Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
![]() Student's Home
Student's Home
![]() Tutor's Home
Tutor's Home
Years of Experience in Class 11 Tuition
7
Board
ISC/ICSE, International Baccalaureate, CBSE, State
Subjects taught
Psychology, Education, Biotechnology, EVS, Geology, History, Hindi, Chemistry, Sociology, Philosophy, Biology, Geography, Logic
Taught in School or College
No
Class Location
![]() Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
![]() Student's Home
Student's Home
![]() Tutor's Home
Tutor's Home
Years of Experience in Class 12 Tuition
7
Board
ISC/ICSE, International Baccalaureate, CBSE, State
Subjects taught
Education, History, Philosophy, Hindi, Psychology, Geology, Geography, Logic, EVS, Biology, Biotechnology, Chemistry, Sociology
Taught in School or College
No
1. Which school boards of Class 10 do you teach for?
State, International Baccalaureate, ICSE and others
2. Do you have any prior teaching experience?
No
3. Which classes do you teach?
I teach Class 10 Tuition, Class 11 Tuition, Class 12 Tuition and Class 9 Tuition Classes.
4. Do you provide a demo class?
Yes, I provide a free demo class.
5. How many years of experience do you have?
I have been teaching for 7 years.
Answered on 27/11/2021 Learn CBSE/Class 11/Science/Chemistry
Chemistry is a very useful subject which can help you personally and professionally. Chemistry is divided into many branches, namely, organic, physical, inorganic, analytical, green, environmental, nuclear, etc. You can perform experiments at home, school and college. You can learn to make many fabrics or crackers or dyes at home as well as in industries. Everyday items like soaps, detergents, paints, clothes, furnishings, hair dyes, etc are made from chemicals. Sanitizers like dettol are also made from chemical ingredients to prevent us from corona virus. Medicines and injections have chemicals as their contents. By learning Chemistry, one can acquire immense knowledge and use it professionally.
Answered on 02/06/2021 Learn CBSE/Class 10/Science
Carbon forms covalent bonds because carbon has an atomic number 6 and have 4 electrons in its octet. So, it can neither lose nor gain 4 electrons to complete its octet. Thus, it forms covalent bonds by sharing its 4 electrons, and covalent bonds are stronger than ionic bonds.
Carbon has atomic number 6. Hence, its electronic configuration is (2,4). In other words, it has two electrons in its first (K) shell and four electrons in its second (L) shell. The carbon atom tries to complete its octet (fill its outermost shell with 8 electrons). But, carbon has to gain either four electrons or lose four electrons. When it gains four electrons, it will acquire four negative charges, and when it loses four electrons, it becomes C+4. C-4 is very unstable as negatively charged carbon repels extra electrons. Since both these forms are very unstable and require much energy, carbon completes its octet by sharing electrons with other atoms and forms covalent bonds. As a result, carbon has the unique capacity of forming chains and branches. Carbon is a tetravalent and covalent element. That is why carbon shares its electron with other elements to form a compound.
Carbon has an atomic number of 6, so it has a valency of 4(2,4). Thus, it can form upto four bonds with each other. This covalency helps carbon in forming a long chain.
Answered on 06/02/2021 Learn Tuition
Sir William Ward put forward the scheme for the Partition of Bengal in 1896. It was proposed to bring efficiency in administration by transferring Dacca, Chittagong and Mymensingh from Bengal to Assam.
The main argument advanced by the British government in favour of Bengal partitioning was administrative convenience, i.e., Bengal was too big a province to be efficiently administered.
But, behind this argument of administrative convenience, the government's real motive was political and economy based.
Based on government papers and secret documents, the expansion of Assam was necessary to the British on economic grounds.
The political motive behind the scheme of partitioning was to curb the rising tide of nationalism in Bengal. By cutting out some portions of Bengal, Lord Curzon (Viceroy) sought to break up Bengalees' political unity.
This was evident from a remark of Risly that 'Bengal united is a power, Bengal divided will pull it in many different directions. Another motive behind the partitioning was to incite the feeling of communalism.
Additionally, it was for creating dispute between Hindus and Muslims of Bengal that the Muslim-dominated region areas were separated from Bengal.
Hindus had been reduced to a minority in the newly-created province of 'Eastern Bengal and Assam'.
Hence, Lord Curzon's government sought to weaken the strength of Bengal by creating division between the two communities - Hindus and Muslims.
Answered on 03/06/2019 Learn CBSE/Class 11/Science/Chemistry/Unit 10-s -Block Elements (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
Answered on 03/06/2019 Learn CBSE/Class 11/Science/Chemistry/Unit 11-Some p -Block Elements
The electronic configuration of Al and Ga are: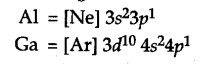
Gallium has 10 additional d-electrons in its inner shell or core of its atom. The presence of additional 10d electrons offer poor screening effect for the outer electrons from the increased charge in gallium (Ga). Consequently, the atomic radius of gallium (135 pm) is less than that of aluminium (143 pm).
Class Location
![]() Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
![]() Student's Home
Student's Home
![]() Tutor's Home
Tutor's Home
Years of Experience in Class 9 Tuition
7
Board
State, International Baccalaureate, ICSE, CBSE
Subjects taught
Biology, Chemistry, Social Science, Geography, EVS, Science, Environmental Applications, History, History and Civics, Hindi
Taught in School or College
No
Class Location
![]() Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
![]() Student's Home
Student's Home
![]() Tutor's Home
Tutor's Home
Years of Experience in Class 10 Tuition
7
Board
State, International Baccalaureate, ICSE, CBSE
Subjects taught
Environmental Applications, Biology, History and Civics, Science, EVS, Hindi, Geography, History, Chemistry, Social Science
Taught in School or College
No
Class Location
![]() Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
![]() Student's Home
Student's Home
![]() Tutor's Home
Tutor's Home
Years of Experience in Class 11 Tuition
7
Board
ISC/ICSE, International Baccalaureate, CBSE, State
Subjects taught
Psychology, Education, Biotechnology, EVS, Geology, History, Hindi, Chemistry, Sociology, Philosophy, Biology, Geography, Logic
Taught in School or College
No
Class Location
![]() Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
Online (video chat via skype, google hangout etc)
![]() Student's Home
Student's Home
![]() Tutor's Home
Tutor's Home
Years of Experience in Class 12 Tuition
7
Board
ISC/ICSE, International Baccalaureate, CBSE, State
Subjects taught
Education, History, Philosophy, Hindi, Psychology, Geology, Geography, Logic, EVS, Biology, Biotechnology, Chemistry, Sociology
Taught in School or College
No
Answered on 27/11/2021 Learn CBSE/Class 11/Science/Chemistry
Chemistry is a very useful subject which can help you personally and professionally. Chemistry is divided into many branches, namely, organic, physical, inorganic, analytical, green, environmental, nuclear, etc. You can perform experiments at home, school and college. You can learn to make many fabrics or crackers or dyes at home as well as in industries. Everyday items like soaps, detergents, paints, clothes, furnishings, hair dyes, etc are made from chemicals. Sanitizers like dettol are also made from chemical ingredients to prevent us from corona virus. Medicines and injections have chemicals as their contents. By learning Chemistry, one can acquire immense knowledge and use it professionally.
Answered on 02/06/2021 Learn CBSE/Class 10/Science
Carbon forms covalent bonds because carbon has an atomic number 6 and have 4 electrons in its octet. So, it can neither lose nor gain 4 electrons to complete its octet. Thus, it forms covalent bonds by sharing its 4 electrons, and covalent bonds are stronger than ionic bonds.
Carbon has atomic number 6. Hence, its electronic configuration is (2,4). In other words, it has two electrons in its first (K) shell and four electrons in its second (L) shell. The carbon atom tries to complete its octet (fill its outermost shell with 8 electrons). But, carbon has to gain either four electrons or lose four electrons. When it gains four electrons, it will acquire four negative charges, and when it loses four electrons, it becomes C+4. C-4 is very unstable as negatively charged carbon repels extra electrons. Since both these forms are very unstable and require much energy, carbon completes its octet by sharing electrons with other atoms and forms covalent bonds. As a result, carbon has the unique capacity of forming chains and branches. Carbon is a tetravalent and covalent element. That is why carbon shares its electron with other elements to form a compound.
Carbon has an atomic number of 6, so it has a valency of 4(2,4). Thus, it can form upto four bonds with each other. This covalency helps carbon in forming a long chain.
Answered on 06/02/2021 Learn Tuition
Sir William Ward put forward the scheme for the Partition of Bengal in 1896. It was proposed to bring efficiency in administration by transferring Dacca, Chittagong and Mymensingh from Bengal to Assam.
The main argument advanced by the British government in favour of Bengal partitioning was administrative convenience, i.e., Bengal was too big a province to be efficiently administered.
But, behind this argument of administrative convenience, the government's real motive was political and economy based.
Based on government papers and secret documents, the expansion of Assam was necessary to the British on economic grounds.
The political motive behind the scheme of partitioning was to curb the rising tide of nationalism in Bengal. By cutting out some portions of Bengal, Lord Curzon (Viceroy) sought to break up Bengalees' political unity.
This was evident from a remark of Risly that 'Bengal united is a power, Bengal divided will pull it in many different directions. Another motive behind the partitioning was to incite the feeling of communalism.
Additionally, it was for creating dispute between Hindus and Muslims of Bengal that the Muslim-dominated region areas were separated from Bengal.
Hindus had been reduced to a minority in the newly-created province of 'Eastern Bengal and Assam'.
Hence, Lord Curzon's government sought to weaken the strength of Bengal by creating division between the two communities - Hindus and Muslims.
Answered on 03/06/2019 Learn CBSE/Class 11/Science/Chemistry/Unit 10-s -Block Elements (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
Answered on 03/06/2019 Learn CBSE/Class 11/Science/Chemistry/Unit 11-Some p -Block Elements
The electronic configuration of Al and Ga are: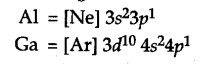
Gallium has 10 additional d-electrons in its inner shell or core of its atom. The presence of additional 10d electrons offer poor screening effect for the outer electrons from the increased charge in gallium (Ga). Consequently, the atomic radius of gallium (135 pm) is less than that of aluminium (143 pm).

Share this Profile
Also have a look at
Reply to 's review
Enter your reply*
Your reply has been successfully submitted.
Certified
The Certified badge indicates that the Tutor has received good amount of positive feedback from Students.