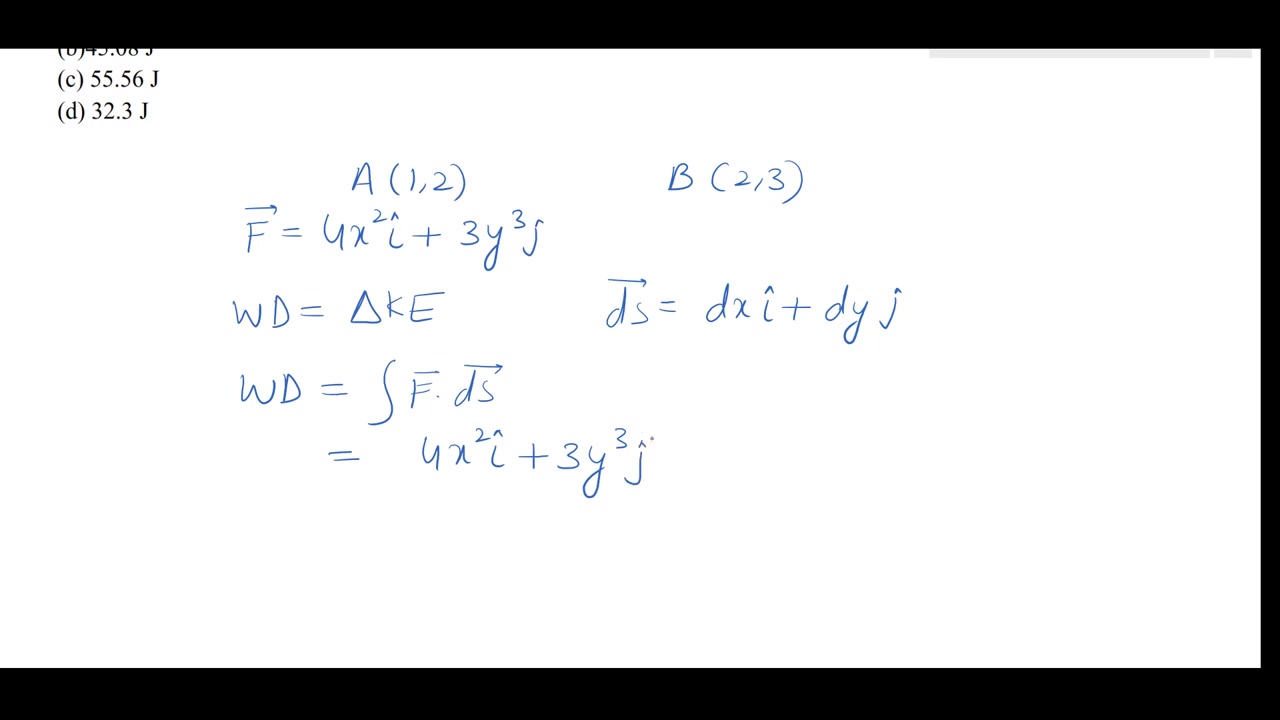Numerical Ability Improvement Course for Better undertanding of Subject and Makes solid foundation for NEET and Jee Exam preparation.
following topics will be discussed in dept in the course.
Unit 1: Physical world
Physics and its laws: Physical world
Unit 2: Units and measurement
Physical quantities and their measurement: Units and measurement
Scientific notation: Units and measurement
Significant figures: Units and measurement
Unit 3: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
Introduction to logarithms: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
The constant e and the natural logarithm: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
Slope: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
Basics of trigonometry: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
The unit circle definition of sine, cosine, and tangent: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
The graphs of sine, cosine, and tangent: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
Basic trigonometric identities: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
Evaluating functions: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
Inputs and outputs of a function: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
Maximum and minimum points: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
Intervals where a function is positive, negative, increasing, or decreasing: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
Interpreting features of graphs: Basic math concepts for physics (Prerequisite)
Unit 4: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Slope: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Introduction to differential calculus: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Secant lines: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Limit basics: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Derivative as a limit: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Using the formal definition of derivative: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Derivative as a function: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Basic differentiation rules: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Power rule: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Polynomial functions differentiation: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Sine & cosine derivatives: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Product rule: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Chain rule: Differentiation for physics (Prerequisite)
Unit 5: Integration for physics (Prerequisite)
Antiderivatives: Integration for physics (Prerequisite)
Indefinite integrals of common functions: Integration for physics (Prerequisite)
Definite integral as area: Integration for physics (Prerequisite)
Riemann sums: Integration for physics (Prerequisite)
Definite integral evaluation: Integration for physics (Prerequisite)
u-substitution: Integration for physics (Prerequisite)
Area & net change: Integration for physics (Prerequisite)
Unit 6: Motion in a straight line
Distance, displacement, and coordinate systems: Motion in a straight line
Average velocity and average speed: Motion in a straight line
Velocity and speed from graphs: Motion in a straight line
Acceleration: Motion in a straight line
Kinematic formulas: Motion in a straight line
Objects in freefall: Motion in a straight line
Rectilinear motion (integral calc): Motion in a straight line
Relative velocity in 1D: Motion in a straight line
Unit 7: Vectors (Prerequisite)
Vector basics: Vectors (Prerequisite)
Magnitude of vectors: Vectors (Prerequisite)
Scalar multiplication: Vectors (Prerequisite)
Vector addition and subtraction: Vectors (Prerequisite)
Combined vector operations: Vectors (Prerequisite)
Unit vectors: Vectors (Prerequisite)
Magnitude and direction form of vectors: Vectors (Prerequisite)
Component form of vectors: Vectors (Prerequisite)
Adding vectors in magnitude and direction form: Vectors (Prerequisite)
Applications of vectors: Vectors (Prerequisite)
Unit 8: Motion in a plane
Introduction to vectors and two-dimensional motion: Motion in a plane
Analyzing vectors using trigonometry: Motion in a plane
Review: Unit vectors: Motion in a plane
Graphs of projectile motion: Motion in a plane
Horizontally launched projectiles: Motion in a plane
Projectiles launched at an angle: Motion in a plane
Projectiles launched from/to a height: Motion in a plane
Optimal angle for a projectile: Motion in a plane
Projectile on an incline: Motion in a plane
Relative motion in 2D: Motion in a plane
Uniform circular motion introduction: Motion in a plane
Centripetal acceleration: Motion in a plane
Unit 9: Laws of motion
Introduction to forces and free body diagrams: Laws of motion
Newton's first law: Mass and inertia: Laws of motion
Newton's second law: Laws of motion
Newton's third law: Laws of motion
Normal force and contact force: Laws of motion
Balanced and unbalanced forces: Laws of motion
Slow sock on Lubricon VI: Laws of motion
Inclined planes: Laws of motion
Friction: Laws of motion
Tension: Laws of motion
Treating systems: Laws of motion
Centripetal forces: Laws of motion
Centripetal force problem solving: Laws of motion
Introduction to linear momentum and impulse: Laws of motion
Conservation of linear momentum and elastic collision: Laws of motion
Collision in 2D: Laws of motion
Unit 10: Work, energy and power
Introduction to work: Work, energy and power
Kinetic energy: Work, energy and power
Work-energy theorem: Work, energy and power
Gravitational potential energy and conservative forces: Work, energy and power
Spring potential energy and Hooke's law: Work, energy and power
Conservation of energy: Work, energy and power
Work and energy problems involving friction: Work, energy and power
Power: Work, energy and power
Elastic and inelastic collisions: Work, energy and power
Unit 11: System of particles and rotational motion
Centre of mass: System of particles and rotational motion
Introduction to rotational motion: System of particles and rotational motion
Angular kinematics: System of particles and rotational motion
Torque and equilibrium: System of particles and rotational motion
Cross product and torque: System of particles and rotational motion
Rotational inertia and angular second law: System of particles and rotational motion
Rotational kinetic energy: System of particles and rotational motion
Angular momentum and angular impulse: System of particles and rotational motion
Conservation of angular momentum: System of particles and rotational motion
Unit 12: Gravitation
Newton's law of gravitation: Gravitation
Gravitational potential energy at large distances: Gravitation
Unit 13: Mechanical properties of solids
Stress, strain, and modulus of elasticity: Mechanical properties of solids
Shear and bulk stress: Mechanical properties of solids
Application of elastic properties (Bonus): Mechanical properties of solids
Unit 14: Mechanical properties of fluid
Density and pressure: Mechanical properties of fluid
Buoyant force and Archimedes' principle: Mechanical properties of fluid
Fluid dynamics: Mechanical properties of fluid
Viscosity: Mechanical properties of fluid
Surface tension: Mechanical properties of fluid
Unit 15: Thermal properties of matter
Measurement of temperature and pressure: Thermal properties of matter
Specific heat and heat transfer: Thermal properties of matter
Modes of heat transfer: Thermal properties of matter
Thermal expansion in solids: Thermal properties of matter
Thermal expansion in fluids: Thermal properties of matter
Thermal stress: Thermal properties of matter
Unit 16: Thermodynamics
Zeroth and first law of thermodynamics: Thermodynamics
Work from PV graph and internal energy: Thermodynamics
Thermodynamic processes and Carnot cycle: Thermodynamics
Unit 17: Kinetic theory
Ideal gas equation: Kinetic theory
Kinetic molecular theory of gases: Kinetic theory
Unit 18: Oscillations
Introduction to simple harmonic motion: Oscillations
Simple harmonic motion in spring-mass systems: Oscillations
Simple pendulums: Oscillations
Energy in simple harmonic oscillators: Oscillations
Simple harmonic motion (with calculus): Oscillations
Unit 19: Waves
Introduction to waves: Waves
Wave characteristics: Waves
Wave interference: Waves
Standing waves: Waves
Sound: Waves
Beats and interference of sound waves: Waves
The Doppler effect
join this course to boost your Physics preparation for NEET and JEE level examination.