Problem: A spinner has 4 equal sectors colored yellow, blue, green and red. What are the chances of landing on blue after spinning the spinner? What are the chances of landing on red?
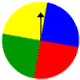
Solution: The chances of landing on blue are 1 in 4, or one fourth.
The chances of landing on red are 1 in 4, or one fourth.
This problem asked us to find some probabilities involving a spinner. Let's look at some definitions and examples from the problem above.
| Definition | Example |
| An experiment is a situation involving chance or probability that leads to results called outcomes. | In the problem above, the experiment is spinning the spinner. |
| An outcome is the result of a single trial of an experiment. | The possible outcomes are landing on yellow, blue, green or red. |
| An event is one or more outcomes of an experiment. | One event of this experiment is landing on blue. |
| Probability is the measure of how likely an event is. | The probability of landing on blue is one fourth. |
In order to measure probabilities, mathematicians have devised the following formula for finding the probability of an event.
| Probability Of An Event | |||
|
The probability of event A is the number of ways event A can occur divided by the total number of possible outcomes. Let's take a look at a slight modification of the problem from the top of the page.
Experiment 1: A spinner has 4 equal sectors colored yellow, blue, green and red. After spinning the spinner, what is the probability of landing on each color?
The possible outcomes of this experiment are yellow, blue, green, and red.
Probabilities:
| P(yellow) | = | # of ways to land on yellow | = | 1 |
| total # of colors | 4 | |||
| P(blue) | = | # of ways to land on blue | = | 1 |
| total # of colors | 4 | |||
| P(green) | = | # of ways to land on green | = | 1 |
| total # of colors | 4 | |||
| P(red) | = | # of ways to land on red | = | 1 |
| total # of colors | 4 | |||
Experiment 2: A single 6-sided die is rolled. What is the probability of each outcome? What is the probability of rolling an even number? of rolling an odd number?
![]()

Outcomes: The possible outcomes of this experiment are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6.
Probabilities:
| P(1) | = | # of ways to roll a 1 | = | 1 | ||
| total # of sides | 6 | |||||
| P(2) | = | # of ways to roll a 2 | = | 1 | ||
| total # of sides | 6 | |||||
| P(3) | = | # of ways to roll a 3 | = | 1 | ||
| total # of sides | 6 | |||||
| P(4) | = | # of ways to roll a 4 | = | 1 | ||
| total # of sides | 6 | |||||
| P(5) | = | # of ways to roll a 5 | = | 1 | ||
| total # of sides | 6 | |||||
| P(6) | = | # of ways to roll a 6 | = | 1 | ||
| total # of sides | 6 | |||||
| P(even) | = | # ways to roll an even number | = | 3 | = | 1 |
| total # of sides | 6 | 2 | ||||
| P(odd) | = | # ways to roll an odd number | = | 3 | = | 1 |
| total # of sides | 6 | 2 | ||||
Experiment 2 illustrates the difference between an outcome and an event. A single outcome of this experiment is rolling a 1, or rolling a 2, or rolling a 3, etc. Rolling an even number (2, 4 or 6) is an event, and rolling an odd number (1, 3 or 5) is also an event.
In Experiment 1 the probability of each outcome is always the same. The probability of landing on each color of the spinner is always one fourth. In Experiment 2, the probability of rolling each number on the die is always one sixth. In both of these experiments, the outcomes are equally likely to occur. Let's look at an experiment in which the outcomes are not equally likely.
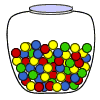 Experiment 3: A glass jar contains 6 red, 5 green, 8 blue and 3 yellow marbles. If a single marble is chosen at random from the jar, what is the probability of choosing a red marble? a green marble? a blue marble? a yellow marble?
Experiment 3: A glass jar contains 6 red, 5 green, 8 blue and 3 yellow marbles. If a single marble is chosen at random from the jar, what is the probability of choosing a red marble? a green marble? a blue marble? a yellow marble?
Outcomes: The possible outcomes of this experiment are red, green, blue and yellow.
Probabilities:
| P(red) | = | # of ways to choose red | = | 6 | = | 3 |
| total # of marbles | 22 | 11 | ||||
| P(green) | = | # of ways to choose green | = | 5 | ||
| total # of marbles | 22 | |||||
| P(blue) | = | # of ways to choose blue | = | 8 | = | 4 |
| total # of marbles | 22 | 11 | ||||
| P(yellow) | = | # of ways to choose yellow | = | 3 | ||
| total # of marbles | 22 | |||||
The outcomes in this experiment are not equally likely to occur. You are more likely to choose a blue marble than any other color. You are least likely to choose a yellow marble.
Experiment 4: Choose a number at random from 1 to 5. What is the probability of each outcome? What is the probability that the number chosen is even? What is the probability that the number chosen is odd?
Outcomes: The possible outcomes of this experiment are 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.
Probabilities:
| P(1) | = | # of ways to choose a 1 | = | 1 |
| total # of numbers | 5 | |||
| P(2) | = | # of ways to choose a 2 | = | 1 |
| total # of numbers | 5 | |||
| P(3) | = | # of ways to choose a 3 | = | 1 |
| total # of numbers | 5 | |||
| P(4) | = | # of ways to choose a 4 | = | 1 |
| total # of numbers | 5 | |||
| P(5) | = | # of ways to choose a 5 | = | 1 |
| total # of numbers | 5 | |||
| P(even) | = | # of ways to choose an even number | = | |


 0
0

