- The standard deviation, s, is a statistical measure of the precision for a series of repeated measurements. The advantage of using s to quote uncertainty in a result is that it has the same units as the experimental data.
- Under a normal distribution, (± one standard deviation) encompasses 68% of the measurements and (± two standard deviations) encompasses 96% of the measurements. Standard deviation is calculated from:
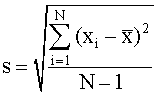
- Where N is the number of measurements, xi is each individual measurement, and
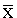 is the mean of all measurements.
is the mean of all measurements. - The quantity (xi -
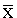 ) is called the "residual" or the "deviation from the mean" for each measurement. The quantity (N - 1) is called the "degrees of freedom" for the measurement.
) is called the "residual" or the "deviation from the mean" for each measurement. The quantity (N - 1) is called the "degrees of freedom" for the measurement.


 0
0

